Know Your Dressings: Hydrogels
Wounds require adequate moisture to heal. Without sufficient moisture, the wound bed may become dry or desiccated, leading to necrotic wound tissue, which can result in a larger, deeper wound.1 Achieving optimal moisture in the wound is a balancing act, a wound bed that is too wet can result in delayed wound healing and periwound maceration, which can increase wound size.2 Modern wound care is individualized; it is based on assessment, which includes the evaluation of moisture levels in the wound.
Moist wound healing concepts have replaced the old one-dressing-fits-all approach of dry gauze dressings. Evidence shows that an appropriate moisture balance in the wound bed speeds wound healing, facilitates autolytic debridement, promotes cell growth and proliferation, speeds angiogenesis and wound contraction. Moist wound healing also reduces pain and decreases scar formation.
Moisture can be controlled in a wound using dressings to enhance healing. Hydrogel dressings provide moisture and are appropriate for wounds that are small or large, full or partial thickness. They can also be used in wounds with necrotic or infected tissue. Hydrogel dressings consist of approximately 90% water in a gel suspension. Properties that make hydrogel dressings the “ideal” dressing for an appropriate wound are their ability to promote healing, cost effectiveness, ease of application and their ability to soothe and reduce pain. Some hydrogel dressings are infused with antimicrobial silver to reduce bacteria in the wound environment.
Hydrogels for Autolytic Debridement
Removing slough or necrotic tissue from the wound bed is a critical element in wound bed preparation. Autolysis is a form of debridement that allows the body’s natural and selective abilities to liquify devitalized tissue. Autolytic debridement is safe and painless. Hydrogel dressings provide a supportive environment that can facilitate the autolytic debridement process.
Hydrogels to Reduce Pain
The high concentration of water in a hydrogel dressing makes it comfortable and soothing. Hydrogel dressings do not irritate tissue, and provide a cooling effect that can be soothing to wounded tissue. The non-adhesive nature of hydrogel minimizes pain, especially with dressing changes.
Types of Hydrogel Dressings
Hydrogel dressings are available as amorphous gels available in spray bottles, tubes or packets, impregnated into gauze, sponge or rope material or as a sheet dressing that maintains its shape. Each type has unique qualities that provide options for wound hydration.
Designed for effectiveness and ease of use, DermaRite has a complete line of advanced hydrogel products.
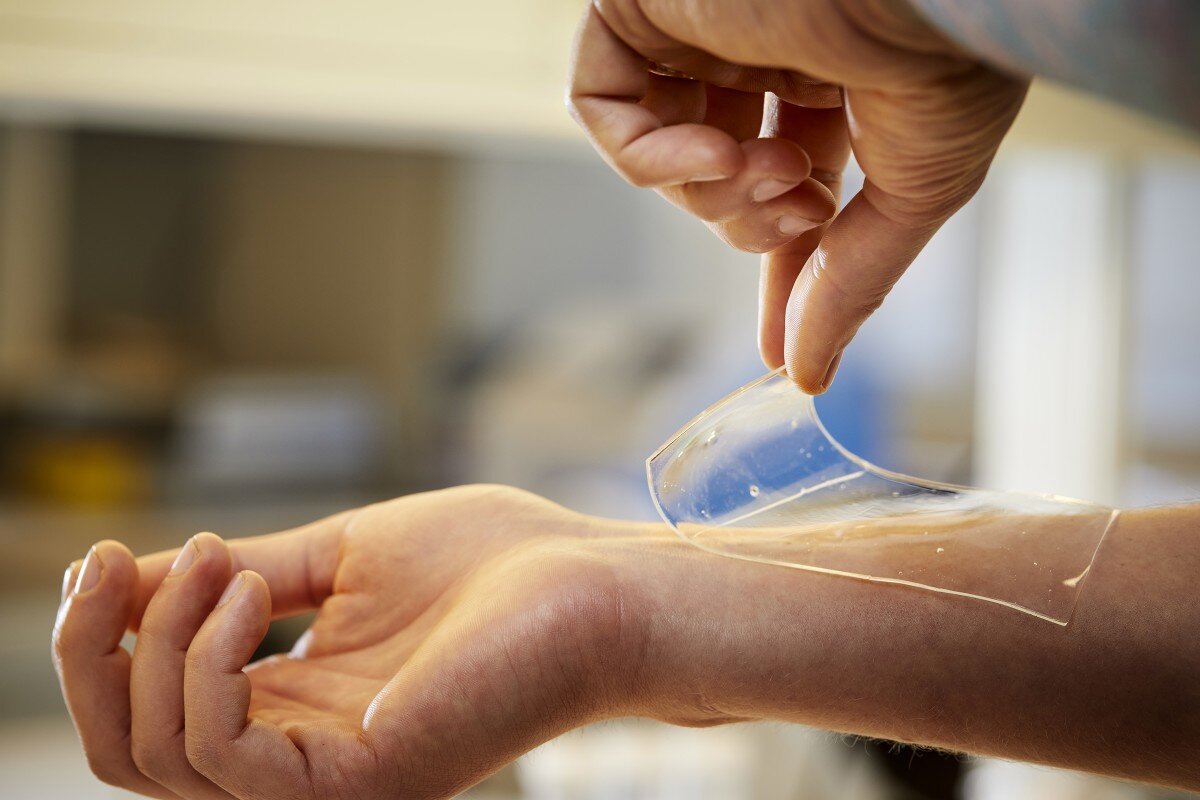
AquaDerm™ is a hydrogel sheet wound dressing with a waterproof backing. Cool and soothing, it reduces local pain in superficial wounds and absorbs moisture from wounds with minimal drainage.
DermaSyn™ is an amorphous hydrogel wound dressing enriched with vitamin E. DermaSyn donates moisture to dry or minimally draining wounds for an optimal moist environment.
DermaSyn/Ag™ is a water-based gel wound dressing which contains ionic silver which has been shown to inhibit the growth of microorganisms.
DermaGauze™ is a hydrogel impregnated gauze dressing. Convenient for gentle packing of dry to minimally draining wounds.